
What is Zero Day Attack? And how it affects any IT industry.
If any software, hardware or firmware has a vulnerability that is not known to the developer or vendor, then it can be a victim of a zero-day attack. Because the vendor has “zero days” to fix the flaw before it is exploited, the term “zero-day attack” fits perfectly. The organisation’s root resides in its data centre, which can be either on-premises or on the cloud, comprising both hardware and software components. Both elements are susceptible to software bugs and vulnerabilities, making them prone to zero-day attacks. Because they can appear as any type of broad software vulnerability, zero-day weaknesses can take almost any form. They might, for instance, be missing data encryption, SQL injection, buffer overflows, missing authorisations, faulty algorithms, URL redirections, bugs, or password security issues.
How Does a Zero-Day Attack Work?
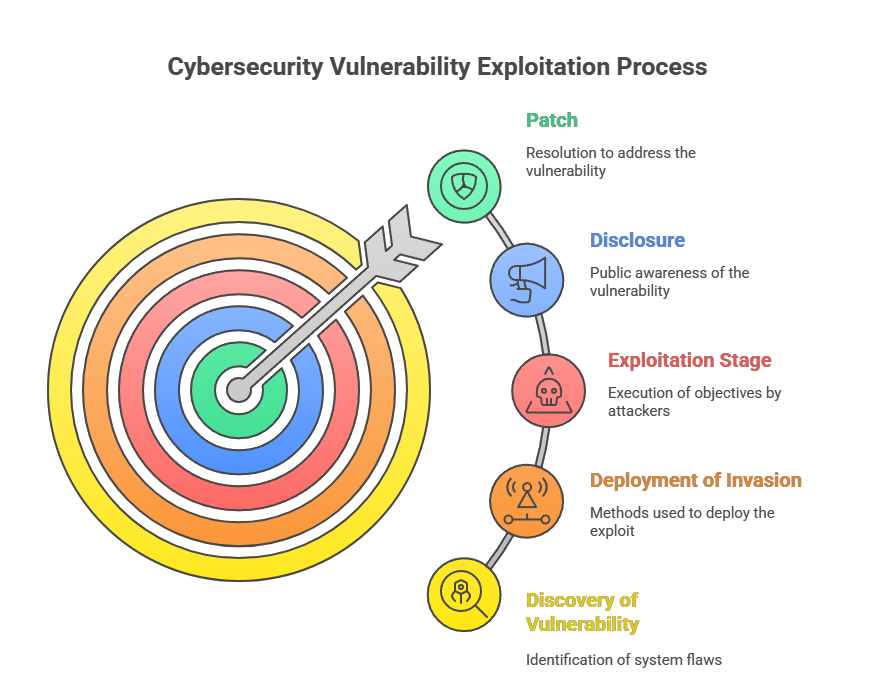
Generally, zero-day attacks follow a known sequence:
- Discovery of Vulnerability: A perpetrator, often a hacker or cybercriminal, determines a flaw in a system that has not yet been noticed.
- Evolution of Exploit: The attacker creates an exploit tailored to gain unauthorised access, exfiltrate data, or disrupt operations through the vulnerabilities.
- Deployment of Invasion: The exploit is deployed through various means such as phishing emails, malicious websites, or infected software updates.
- Exploitation Stage: Attackers use the vulnerability to execute their objectives until the flaw is detected and addressed by the vendor.
- Disclosure: The defect becomes publicly known. This is the best process where security researchers or ethical hackers report vulnerabilities to the relevant institution, giving them time to fix the issue before it’s made public.
- Patch: To address the weakness, developers work on releasing the resolution without mandating a complete overhaul or upgrade.
Why Are Zero-Day Attacks So Dangerous?
Lack of Awareness and Preparedness
The nature of zero-day vulnerabilities means nobody knows they exist until it’s too late. This blindsides both users and developers, and it is mainly due to the lack of prior knowledge and preparedness.
Exploitation Before Detection
Foes operate swiftly, manipulating vulnerabilities before patches can be released. It’s a race against time, and unfortunately, hackers often succeed in the first round.
Global Impact of Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day attacks can shut down hospitals, compromise essential infrastructure, or expose government data. Their ripple consequence is deemed globally.